Subdued demand leads to further moderation of Malaysia's manufacturing sector

Malaysia's manufacturing sector continued to face challenging business conditions in the final month of 2022.
马来西亚的制造业在 2022 年的最后一个月继续面临充满挑战的商业环境。
S&P Global in its Malaysia Manufacturing PMI note on 3rd January said that muted customer demand reportedly contributed to sustained moderations in output and order books.
标普全球在1 月 3 日的马来西亚制造业 PMI 报告中表示,据报道,客户需求疲软导致产量和订单持续放缓。
It said companies subsequently trimmed input buying and downwardly adjusted inventory levels.
它表示,公司随后削减了投入品购买并下调了库存水平。
Backlogs of work, meanwhile, depleted at a rate among the fastest on record.
与此同时,积压的工作以有记录以来最快的速度耗尽。
Some more positive developments within the latest survey data came from cost and supply pressures both easing.
最新调查数据中的一些更积极的发展来自成本和供应压力的缓解。
Vendor performance stabilised in December, ending the three-year sequence of deterioration, and firms cut their selling prices for the first time since May 2020.
供应商业绩在 12 月趋于稳定,结束了连续三年的恶化,公司自 2020 年 5 月以来首次下调了售价。
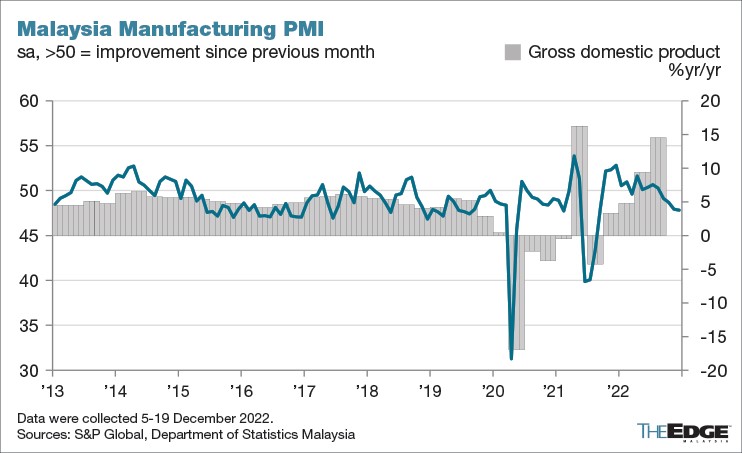
The seasonally adjusted S&P Global Malaysia Manufacturing Purchasing Managers' Index posted at 47.8 in December, slipping from 47.9 in November to mark a fourth consecutive softening of operating conditions across the Malaysian manufacturing sector.
经季节性调整的标准普尔全球马来西亚制造业采购经理人指数从 11 月份的 47.9 下滑至 12 月份的 47.8,标志着马来西亚制造业的经营状况连续第四次疲软。
The latest moderation, though broadly in line with that seen in November, was the strongest since August 2021.
最新的放缓虽然与 11 月的情况大体一致,但却是 2021 年 8 月以来最强劲的一次。
Averaging 48.1 over the final quarter of the year, the PMI is representative of approximately 5% year-on-year growth of GDP in Malaysia, thereby representing some loss of momentum from the situation in the third quarter.
今年最后一个季度平均为 48.1,PMI 代表马来西亚国内生产总值同比增长约 5%,因此表明第三季度的势头有所减弱。
Similar to each of the three months prior, a running theme within the latest survey data was fragile customer demand.
与三个月前的每个月类似,最新调查数据中的一个运行主题是脆弱的客户需求。
New orders and foreign demand both moderated in December, stretching the current sequences of reduction to four and six months, respectively.
新订单和国外需求在 12 月双双放缓,将当前的减少顺序分别延长至四个月和六个月。
Reflecting the softer inflows of new work, Malaysian manufacturing firms scaled back production volumes in the final month of the year.
反映新工作流入疲软,马来西亚制造公司在今年最后一个月缩减了产量。
The rate of moderation was slightly steeper than in November and the joint-sharpest since March.
缓和速度比 11 月略陡,是自 3 月以来的联合最急剧。
Companies subsequently trimmed back purchasing activity in December and at a solid pace overall.
公司随后在 12 月削减了采购活动,并且整体步伐稳健。
Lower purchasing and efforts to limit stock holdings amid the current lull in demand fed through to a reduction in pre-production inventories.
在当前需求低迷的情况下,减少采购和限制库存的努力导致生产前库存减少。
This was also the case for post-production inventories where firms reportedly favoured the use of existing stock when fulfilling new orders.
这也是生产后库存的情况,据报道,公司在履行新订单时更喜欢使用现有库存。
Concurrently, employment softened for the second time in the past three months.
同时,就业在过去三个月中第二次出现疲软。
Survey respondents primarily attributed lower staffing levels to voluntary resignations.
调查受访者主要将较低的人员配置水平归因于自愿辞职。
Despite the scaling back in output, there was evidence of spare capacity within the Malaysian manufacturing sector.
尽管产出缩减,但有证据表明马来西亚制造业存在闲置产能。
Firms continued to clear backlogs of work, thereby extending the current sequence of moderation to seven months.
公司继续清理积压的工作,从而将当前的缓和顺序延长至七个月。
Notably, the rate of reduction was among the sharpest on record and the joint-fastest since July 2017.
值得注意的是,降幅是有记录以来的最高降幅之一,也是自 2017 年 7 月以来的最快降幅。
Anecdotal evidence suggested that the latest moderation stemmed from the reduction in order book volumes.
轶事证据表明,最近的缓和源于订单量的减少。
Manufacturers were confident of a rise in production over the coming 12 months, with some firms hopeful that market conditions would improve in the new year.
制造商对未来 12 个月的产量增长充满信心,一些公司希望市场状况在新的一年有所改善。
That said, concerns over the potential for demand conditions to remain muted in 2023 meant that business sentiment remained relatively subdued in December, posting below the historical average.
尽管如此,对 2023 年需求状况可能保持低迷的担忧意味着 12 月的商业信心仍然相对低迷,低于历史平均水平。
S&P Global Market Intelligence's Laura Denman said with muted customer demand remaining a key theme within December's PMI data, the Malaysian manufacturing sector registered a further loss in momentum in the final month of 2022.
S&P Global Market Intelligence 的 Laura Denman 表示,由于客户需求疲软仍然是 12 月 PMI 数据的一个关键主题,马来西亚制造业在 2022 年的最后一个月进一步失去了动力。
She said the moderation in order book volumes, though slightly softer than in November, remained stronger than the average for the year as a whole which subsequently led firms to scale back production at a solid pace.
她表示,订单量的放缓虽然比 11 月份略有放缓,但仍强于全年平均水平,随后导致企业稳步缩减生产。
“Forward looking indicators suggested that firms were anticipating conditions to remain challenging in the coming months as signalled by a further trimming in input buying, reductions in inventory levels and a relatively weak outlook on output over the next year.
“前瞻性指标表明,企业预计未来几个月的情况仍将充满挑战,这体现在进一步削减投入购买、库存水平下降以及明年产出前景相对疲软。
"However, with demand subdued, supplier performance has been able to recover somewhat with December data marking no-change in delivery time from the month prior - following a three-year sequence where delivery times have lengthened on a monthly basis.
“然而,随着需求低迷,供应商的表现已经有所恢复,12 月份的数据表明交货时间与前一个月相比没有变化——此前连续三年交货时间逐月延长。
“Latest survey data was also indicative of an easing in cost pressures.
“最新的调查数据也表明成本压力有所缓解。
“Input costs rose at the slowest pace in the current 31-month sequence of inflation and prices charged by Malaysian manufacturing firms fell for the first time since May 2020,” she said.
她说:“在当前 31 个月的通货膨胀序列中,投入成本以最慢的速度上涨,而马来西亚制造公司收取的价格自 2020 年 5 月以来首次下跌。”
