BNM may front-load more OPR hikes in 2023 to tackle core inflation, say economists

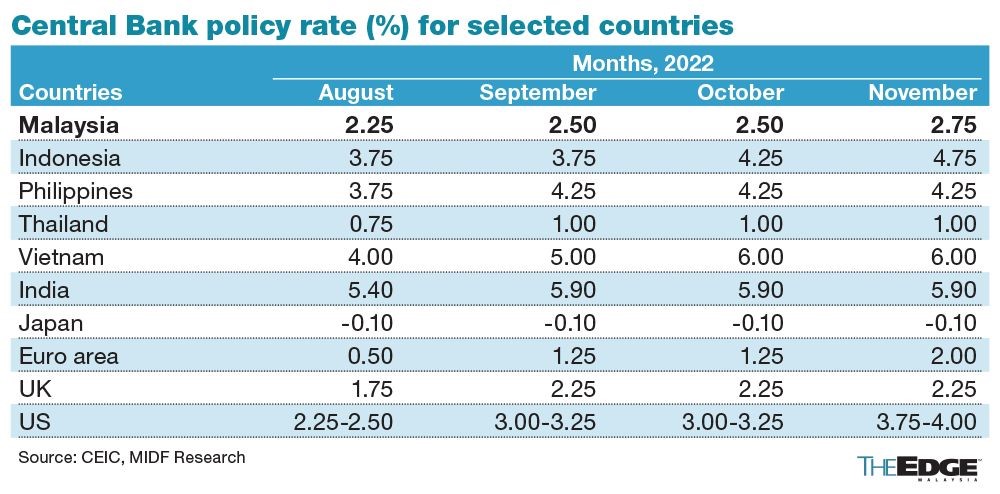
Malaysia’s cost of borrowing increased for the fourth time this year as Bank Negara Malaysia (BNM) hiked the Overnight Rate Policy (OPR) by another 25 basis points (bps) to 2.75% at the sixth and final Monetary Policy Meeting (MPC) for 2022.
随着马来西亚央行(BNM)在2022年第6次也是最后一次货币政策会议(MPC)上将隔夜利率政策(OPR)再上调25个基点(基点)至2.75%,马来西亚的借贷成本今年第四次上升。
Though the hike was widely anticipated by the market, the central bank is far from done and remains keen to rein in inflation by continuing to increase OPR next year until it reaches a neutral rate of 3.25%-5%.
尽管市场普遍预期加息,但央行远未完成,仍热衷于通过明年继续提高 OPR 直至达到 3.25%-5% 的中性利率来控制通胀。
According to economists and fund managers, although BNM may not be emulating the hawkish stance the US Federal Reserve (Fed) took by raising policy rates by a big quantum of 75bps to battle inflation, the central bank may have a much more calculated approach.
根据经济学家和基金经理的说法,尽管BNM可能不会效仿美联储(Fed)采取的鹰派立场,即大幅提高政策利率 75 个基点以对抗通胀,但央行可能有一个更深思熟虑的方法。
Nevertheless, BNM is concerned about the core inflation rate which increased to 4% year-on-year at the end of September 2022, which is a sharp contrast to the 1.6% recorded by the Department of Statistics Malaysia (DOSM) in January, 2022. In August 2022 core inflation reached 3.8%.
尽管如此,BNM担心核心通胀率在2022年9月底同比上升至4%,这与马来西亚统计局(DOSM)在2022年1月记录的1.6%形成鲜明对比。2022年8月,核心通胀率达到3.8%。
The market can anticipate more policy rate increases in 2023, as the central bank strives to achieve the price stability goal, said Sunway University Business School professor of economics Dr Yeah Kim Leng.
双威大学商学院经济学教授Yeah Kim Leng博士表示,随着央行努力实现价格稳定目标,市场可以预期到2023年会有更多的政策加息。
“The increase will help to moderate demand pressures, so that inflation expectations can be managed without resulting in higher inflation.
“这一增长将有助于缓解需求压力,从而可以在不导致通胀上升的情况下管理通胀预期。
“However, given that the interest rate is still below the neutral rate, we expect the central bank to continue its normalisation given that the pre-pandemic interest rate ranged between 3.25% and 5%. We may see the central bank continue to push towards raising the interest rate to the neutral rate. Of course, the quantum and the pace will be based on prevailing inflation as well as growth momentum,” said Dr Yeah when contacted by The Edge CEO Morning Brief.
“然而,鉴于利率仍低于中性利率,鉴于疫情前的利率区间在3.25%至5%之间,我们预计央行将继续其正常化。我们可能会看到中央银行继续推动将利率提高到中性利率。当然,数量和速度将基于当前的通货膨胀和增长势头,” Yeah博士在接受the Edge首席执行官Morning Brief采访时表示。
He added that inflation is not a problem exclusive to Malaysia, as the magnitude of the inflation rate surge has caught many central banks across the world by surprise.
他补充说,通货膨胀并不是马来西亚独有的问题,因为通货膨胀率飙升的幅度令世界各地的许多中央银行感到意外。
“Although the central bank does not have an inflation target, a comfortable inflation level will be around 2.5%-3.5%. But we also note that inflation will remain elevated in the post pandemic environment as well as supply chain disruption caused by the Russia-Ukraine war," said Sunway’s Dr Yeah.
“尽管央行没有通胀目标,但舒适的通胀水平将在 2.5%-3.5% 左右。但我们也注意到,在大流行后的环境以及俄罗斯-乌克兰战争造成的供应链中断后,通胀将继续居高不下,”双威的Yeah博士说。
BNM in a statement on 3rd November said that countries around the world continue to embark on contractionary monetary policies to manage inflationary pressure particularly driven by strong demand and tight labour market.
BNM在 11 月 3 日的一份声明中表示,世界各国继续采取紧缩货币政策来管理通胀压力,特别是在强劲需求和劳动力市场紧张的推动下。
The central bank also highlighted global growth will face challenges from tightening monetary policy in many economies, elevated inflationary pressure in developed markets and domestic challenges in China.
央行还强调,全球增长将面临许多经济体收紧货币政策、发达市场通胀压力上升以及中国国内挑战的挑战。
“We view the decision to raise OPR by another 25bps is timely, taking advantage of the stronger-than-expected macroeconomic performances,” said MIDF Research in an economic review note on 3rd November.
MIDF Research 在 11 月 3 日的经济评论报告中表示:“我们认为,利用好于预期的宏观经济表现,将 OPR 再上调 25 个基点的决定是及时的。”
MIDF added that although BNM views inflation to be manageable in the first nine months of 2022, BNM sees headline and core inflation to stay elevated amid both demand and cost pressures, and possible changes in domestic policy measures in 2023.
MIDF 补充说,尽管BNM认为 2022 年前九个月的通胀是可控的,但在需求和成本压力以及 2023 年国内政策措施可能发生变化的情况下,国行认为整体通胀和核心通胀将保持高位。
“We are in tune with BNM, especially the stance of the post-GE15 (15th general election) government on fuel subsidy policy will determine the direction of Malaysia’s inflation outlook for next year,” said the research firm.
“我们与BNM保持一致,尤其是 GE15(第 15 届大选)后政府对燃料补贴政策的立场,将决定马来西亚明年通胀前景的方向,”该研究公司表示。
MIDF, however, said the OPR increase is also done at a measured pace as the central bank hinted at a strong and robust third quarter gross domestic product (GDP) growth underpinned by improvements in labour market conditions and income prospects.
然而,MIDF 表示,由于劳动力市场状况和收入前景的改善,央行暗示第三季度国内生产总值 (GDP) 增长强劲而强劲,因此 OPR 的增长也以适度的速度进行。
Malaysia GDP expanded by 8.9% in the second quarter of 2022 amid improving domestic demand.
由于国内需求改善,马来西亚 2022 年第二季度 GDP 增长 8.9%。
“With the rising core inflation trend and stronger-than-expected domestic demand, we expect the central bank to front-load its monetary bullets to pre-pandemic levels at 3% by Jan 2023.
“随着核心通胀趋势上升和国内需求强于预期,我们预计央行将在 2023 年 1 月之前将其货币子弹量提前增加至疫情前的水平,即 3%。
“However, the decision will be subject to the stability of economic growth, the pace of price increases and further improvement in macroeconomic conditions, particularly continued recovery in the labour market and growing domestic demand,” said MIDF.
“但是,这一决定将取决于经济增长的稳定性、物价上涨的速度以及宏观经济状况的进一步改善,特别是劳动力市场的持续复苏和国内需求的增长,”MIDF 表示。
From a medium-term perspective, the research outfit said that policy rate normalisation is necessary to avoid risks that could destabilise the future economic outlook such as persistently high inflation and a further rise in household debt.
从中期来看,该研究机构表示,政策利率正常化对于避免可能破坏未来经济前景稳定的风险(例如持续高通胀和家庭债务进一步上升)是必要的。
Ringgit under pressure on Fed’s 75bps rate hike
美联储加息75个基点令令吉承压
On 2nd November, Fed chair Jerome Powell, as widely expected, lifted the policy Fed Funds Target rate (FFTR) by a fourth consecutive 75bps hike to 3.75%-4%.
11 月 2 日,美联储主席Jerome Powell一如市场预期,将政策联邦基金目标利率 (FFTR) 连续第四次上调 75 个基点至 3.75%-4%。
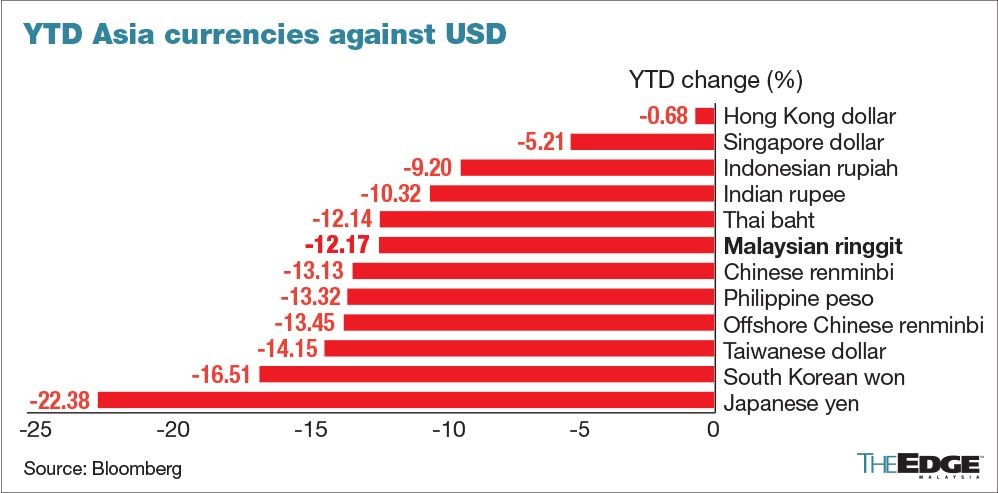
The jumbo interest rate hike may further accelerate the rate of exodus of capital from Asian economies that are still suffering from the consequences of a strong US dollar.
大幅加息可能会进一步加快亚洲经济体的资本外流速度,这些经济体仍在遭受美元走强的影响。
According to Fortress Capital Asset Management Sdn Bhd CEO Thomas Yong, the ringgit is likely to continue to weaken against the US dollar if the interest rate differential between the US dollar and ringgit continues to widen.
Fortress Capital Asset Management Sdn Bhd 首席执行官 Thomas Yong 表示,如果美元和令吉之间的利差继续扩大,令吉兑美元可能会继续走弱。
“Having said that, the strength or weakness of the ringgit is likely to move in line with regional currencies given the strong trade relations regionally,” he told The Edge CEO Morning Brief.
“话虽如此,鉴于区域内强劲的贸易关系,令吉的强弱可能会与区域货币一致,”他告诉 The Edge 首席执行官 Morning Brief。
He added: “The US dollar strengthening has been universally observed against all currencies, rather than just the ringgit. At some point, concerns of a runaway US dollar exchange rate will subside and real transactional demand should then set the rate of exchange.”
他补充说:“普遍观察到美元兑所有货币走强,而不仅仅是林吉特。在某个时候,对美元汇率失控的担忧会消退,然后应该由实际交易需求决定汇率。”
The ringgit continued to fall against the US dollar on Thursday following the Fed’s rate hike due to weak sentiment amid the strengthening greenback.
由于美元走强导致市场情绪疲软,美联储加息后,令吉兑美元周四继续下跌。
At 6pm on 3rd November, the local note fell to 4.7425/7460 versus the US dollar from 4.7360/7400 at Wednesday's close.
11 月 3 日下午 6 点,当地纸币兑美元汇率从周三收盘时的 4.7360/7400 跌至 4.7425/7460。
To date the ringgit has declined 13.72% against the US dollar year to date (YTD).
迄今为止,令吉兑美元年初至今(YTD)已下跌 13.72%。
The Fed also signalled that it will continue to do a few rounds of hikes, which will further exacerbate pressure on the local unit.
美联储还暗示将继续进行几轮加息,这将进一步加剧当地单位的压力。
“With the Fed signalling a more hawkish rate hike path, we maintain our expectation for the ringgit to depreciate further towards the end of the year and average USD/RM4.44 (YTD: USD/RM 4.38),” said RHB Research in a note.
“随着美联储发出更加鹰派的加息路径,我们维持对林吉特在年底前进一步贬值的预期,平均美元/RM4.44(年初至今:美元/RM 4.38),” RHB研究在一份报告中表示。
Widened interest rate differential between US dollar and ringgit risks money outflow
美元与令吉利差扩大风险资金外流
Sunway University’s Dr Yeah added the widening of interest rate differentials against the US interest rate is expected to result in further outflow of foreign funds.
双威大学的Yeah博士补充说,与美国利率的利差扩大预计将导致外国资金进一步流出。
“The US dollar is also known as a safe haven, so we’ll see more funds fleeing there. However it will also be determined by the higher returns there that investors can receive from investing in the US market,” he said.
“美元也被称为避风港,因此我们将看到更多资金逃离那里。然而,这也将取决于投资者从投资美国市场获得的更高回报,”他说。
The foreign demand for Malaysian Government Securities (MGS) and Government Investment Securities (GII) weakened in September, with net outflows of RM2.5 billion in light of the US Fed's continued aggressive stance in raising interest rates.
鉴于美联储在加息方面的持续激进立场,9 月份外国对马来西亚政府证券(MGS)和政府投资证券(GII)的需求减弱,净流出 25 亿令吉。
The 10-year US Treasury (UST) yield jumped 68bps month-on-month to 3.83% as of end-September, outpacing the 10-year MGS yield which rose 45.7bps to 4.44% as of the same date, according to RAM Rating Services Bhd (RAM Ratings) in a report released on 18th October.
根据 RAM Rating 的数据,截至 9 月底,10 年期美国国债(UST)收益率环比上涨 68 个基点至 3.83%,超过了 10 年期 MGS 收益率(截至同日上涨 45.7 个基点至 4.44%) Services Bhd (RAM Ratings) 在 10 月 18 日发布的报告中。
“This is inevitable. But the comfort for Malaysia is we do have sufficient domestic liquidity to offset expected foreign capital outflow. So that will help to maintain the stability in the financial market,” said Dr Yeah.
“这是不可避免的。但令马来西亚感到欣慰的是,我们确实有足够的国内流动性来抵消预期的外国资本外流。因此,这将有助于维持金融市场的稳定,” Yeah博士说。
Fortress’ Yong believes that although the weaker ringgit added pessimism to the financial market, businesses, particularly exporters with cost structure denominated in ringgit, are likely to continue to enjoy the strong US dollar environment.
Fortress' Yong认为,虽然令吉疲软给金融市场增添了悲观情绪,但企业,尤其是以令吉计价的成本结构的出口商,可能会继续享受美元走强的环境。
“However, with global growth expected to slow down ahead, demand might be affected. Sectors such as automobile, airlines, media and pharmaceuticals would likely be affected by the weak ringgit if they cannot pass through the higher costs to the consumers. Generally, those companies with high costs denominated in US dollars would suffer,” he added.
“然而,随着全球增长预计将放缓,需求可能会受到影响。如果汽车、航空、媒体和制药等行业不能将较高的成本转嫁给消费者,它们可能会受到令吉疲软的影响。一般来说,那些以美元计价的高成本公司会受到影响,”他补充说。
