APAC’s growth trajectory in 2023 hinges on China’s recovery; tighter funding and geopolitics to define the year — Moody’s

Strong but moderating economic growth rates in Asia Pacific (APAC) will support the region's credit conditions for 2023, though its growth trajectory will partly hinge on China's recovery, according to Moody’s Investor Service.
据穆迪投资者服务公司称,亚太地区 (APAC) 强劲但放缓的经济增长率将支持该地区 2023 年的信贷状况,尽管其增长轨迹将部分取决于中国的复苏。
"Economic activity will normalise closer to potential levels in most of the region's major economies, while we expect an acceleration in activity in China as authorities lift Covid-related mobility restrictions. However, China's troubled property sector and weaker global demand pose risks to regional growth, with the potential for further geopolitical shocks to ripple through to the supply and prices of key commodities," said Moody's in a statement.
“该地区大多数主要经济体的经济活动将恢复正常,接近潜在水平,而我们预计随着当局取消与新冠病毒相关的流动限制,中国的经济活动将加速。然而,中国陷入困境的房地产行业和疲软的全球需求对区域增长构成风险,进一步的地缘政治冲击有可能波及主要商品的供应和价格,”穆迪在一份声明中表示。
Meanwhile, monetary tightening could slow as inflation peaks, it noted, but external financial conditions will challenge high-yield issuers.
同时,它指出,随着通胀达到顶峰,货币紧缩可能会放缓,但外部金融状况将对高收益发行人构成挑战。
"APAC has largely weathered the inflation shocks emanating from the military conflict between Russia and Ukraine, while central banks have gradually narrowed their policy rate differentials with the US Federal Reserve. Nevertheless, higher dollar financing costs and tighter liquidity will be a strain for Asian high-yield issuers facing maturities in 2023-24, including some frontier sovereigns and Chinese property developers."
“亚太地区在很大程度上经受住了俄罗斯和乌克兰之间军事冲突带来的通胀冲击,而各国央行已逐渐缩小与美联储的政策利差。然而,美元融资成本上升和流动性收紧将对亚洲高企构成压力- 2023-24 年面临到期的收益发行人,包括一些前沿主权国家和中国房地产开发商。”
Minimal risks from currency depreciation but APAC issuers dependent on foreign-currency debts will still be challenged
货币贬值的风险很小,但依赖外币债务的亚太地区发行人仍将面临挑战
Currency weakness in APAC has been pronounced amid the US dollar’s broad strength, it noted, but slowing policy-rate tightening in the US and Europe will alleviate currency pressures for both higher-rated sovereigns and lower-rated ones.
它指出,在美元广泛走强的情况下,亚太地区的货币疲软已经很明显,但美国和欧洲政策利率收紧的放缓将减轻高评级主权国家和低评级主权国家的货币压力。
Currency depreciation poses minimal risks, it said, but will still challenge APAC issuers dependent on foreign-currency debt or local-currency revenue.
它表示,货币贬值带来的风险很小,但仍将挑战依赖外币债务或本币收入的亚太地区发行人。
"Most APAC companies are well protected from recent dollar strength through foreign-currency-linked revenue, while increased local-currency financing provides buffers for some sovereigns. Issuers dependent on local-currency revenue in weaker currencies are the most exposed," it said.
“通过与外币挂钩的收入,大多数亚太地区公司都受到了近期美元走强的保护,而本币融资的增加为一些主权国家提供了缓冲。依赖本币收入的发行人面临的风险最大,”它说。
Advanced economies such as Australia, Japan, South Korea and New Zealand, which experienced depreciation pressures in the second half of 2022, benefit from free-floating currencies and tend to have highly stable local-currency funding bases or large external buffers.
澳大利亚、日本、韩国和新西兰等发达经济体在 2022 年下半年经历了贬值压力,它们受益于自由浮动的货币,往往拥有高度稳定的本币融资基础或庞大的外部缓冲。
In a downside scenario in which growth prospects in China weaken further, depreciation pressures on the renminbi risk will create competitive disadvantages for other exporters in the region such as Malaysia, Thailand and Vietnam, it noted.
它指出,在中国增长前景进一步减弱的下行情况下,人民币贬值风险的压力将对该地区的其他出口商(如马来西亚、泰国和越南)造成竞争劣势。
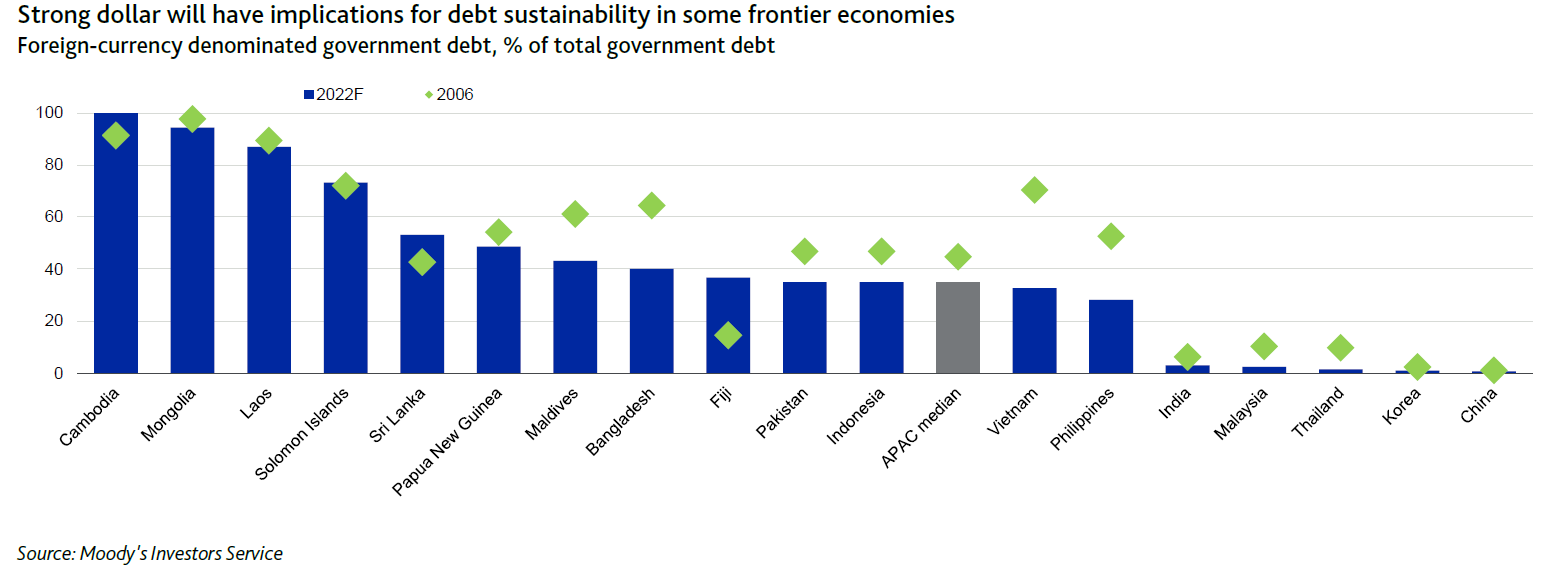
"Most APAC governments have reduced their exposure to foreign-currency-denominated borrowings since before the global financial crisis, although several frontier market sovereigns maintain very high levels of foreign currency debt, including Cambodia, Laos and Mongolia. For stronger-rated sovereigns, the development of deep local-currency bond markets and more flexible exchange rates following the 1997 Asian financial crisis are mitigating factors to bouts of currency depreciation. The prevalence of highly concessional foreign-currency lending by multilateral and bilateral lenders is another mitigating factor.
“自全球金融危机爆发以来,大多数亚太地区政府都减少了外币计价借款的敞口,尽管包括柬埔寨、老挝和蒙古在内的几个前沿市场主权国家的外币债务水平仍然很高。对于评级较高的主权国家, 1997 年亚洲金融危机后本币债券市场的深度发展和更灵活的汇率是货币贬值的缓和因素。多边和双边贷款机构普遍提供高度优惠的外币贷款是另一个缓和因素。
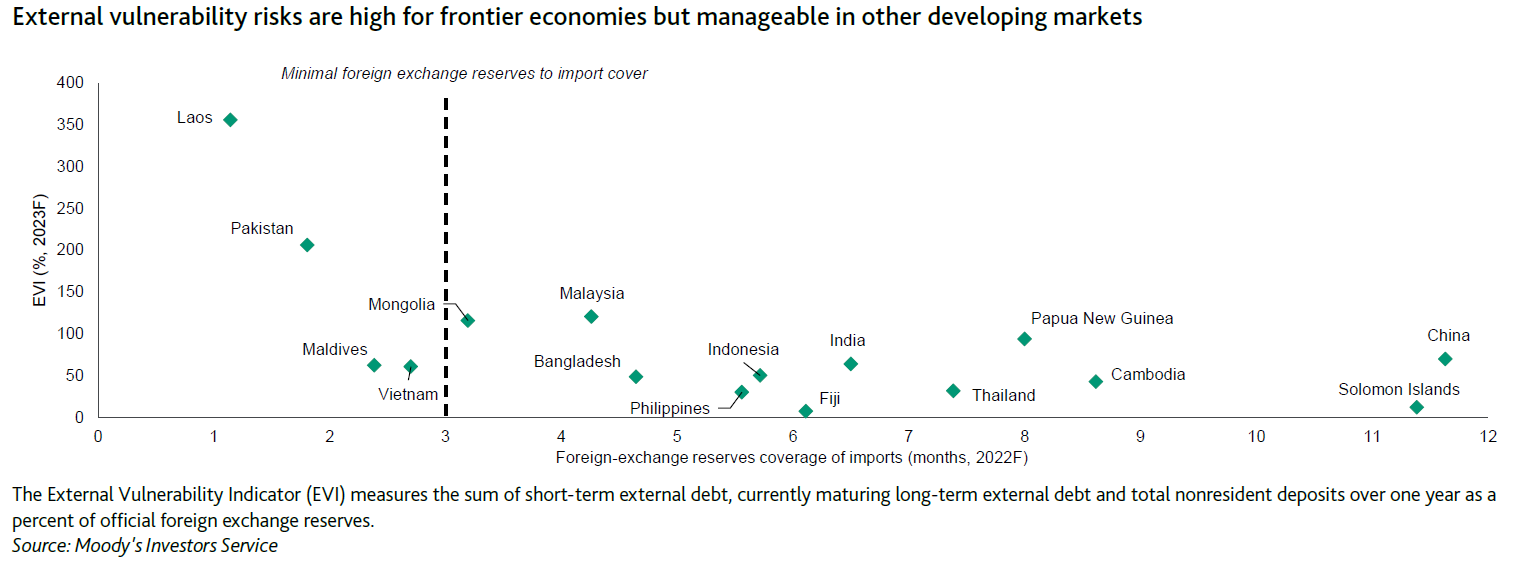
"However, there will be wide differences between economies in their abilities to smooth currency volatility. Most large emerging economies with current account deficits, such as India and Indonesia, continue to hold robust foreign-exchange buffers while reserves adequacy is at critically low levels relative to short-term external liabilities in Laos, Mongolia, Pakistan and, to a lesser degree, Maldives," it noted.
“然而,各经济体在平息货币波动方面的能力存在很大差异。大多数经常账户赤字的大型新兴经济体,如印度和印度尼西亚,继续保持强大的外汇缓冲,而储备充足率处于相对较低的临界水平老挝、蒙古、巴基斯坦的短期外债,以及在较小程度上,马尔代夫的短期外债,”它指出。
Geopolitical fault lines to increase risks of shocks and supply-chain reshaping
地缘政治断层线增加了冲击和供应链重塑的风险
Rising geopolitical tensions in APAC against the backdrop of rising competition between China and the US and its allies in the region will create what Moody's has termed as “fault lines”.
在中美及其地区盟友竞争加剧的背景下,亚太地区地缘政治紧张局势加剧,将形成穆迪所谓的“断层线”。
"These fractures will reflect the formation and evolution of geopolitical alliances and the reconfiguration of APAC’s established economic, trade and financial relationships, with the potential for long-lasting credit effects. These fault lines will pressure international companies, investors and financial institutions to reshape or build redundancy into their operations and relocate supply chains closer to their home markets as geopolitical relations increasingly influence economic and financial connectivity. This is likely to increase operational costs to businesses and drive higher inflation.
“这些裂痕将反映地缘政治联盟的形成和演变,以及亚太地区已建立的经济、贸易和金融关系的重新配置,并可能产生长期的信贷效应。这些断层线将迫使国际公司、投资者和金融机构重塑或随着地缘政治关系对经济和金融连通性的影响越来越大,在他们的运营中建立冗余并将供应链重新安置到更靠近本国市场的位置。这可能会增加企业的运营成本并推高通胀。
US-China tensions will be among the most significant sources of fault line formation in the region, which was illustrated by new US restrictions on China’s access to semiconductor technology and tools, Moody's said.
穆迪表示,美中紧张局势将成为该地区断层线形成的最重要来源之一,美国对中国获取半导体技术和工具的新限制说明了这一点。
"These restrictions will have broad consequences for companies based in Japan, South Korea, Malaysia and Taiwan, China among others," it added.
“这些限制将对日本、韩国、马来西亚和中国台湾等地的公司产生广泛影响,”它补充说。
